Thermal Insulation: Enhancing Energy Efficiency in Buildings
Thermal insulation is a critical component in the construction and retrofitting of buildings, playing a pivotal role in enhancing energy efficiency, reducing utility costs, and promoting sustainable living. By understanding the principles and benefits of thermal insulation, homeowners, builders, and architects can make informed decisions that contribute to a more comfortable, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly built environment.
Understanding Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation refers to materials and techniques used to reduce the transfer of heat between the inside and outside of a building. This process is crucial in maintaining consistent indoor temperatures, regardless of external weather conditions. The effectiveness of insulation is often measured by its R-value, which indicates the material’s resistance to heat flow; higher R-values represent better insulating properties.
Types of Insulation Materials
Various materials are used for thermal insulation, each with unique properties and applications:
- Fiberglass: Widely used due to its affordability and effectiveness, fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers and is commonly installed in batts or rolls.
- Foam Insulation: Available in rigid boards or spray foam, this type offers high R-values and is excellent for sealing gaps and preventing air leaks.
- Cellulose: Made from recycled paper products, cellulose is an eco-friendly option that provides good thermal performance and soundproofing.
- Mineral Wool: Also known as rock wool or slag wool, this material is fire-resistant and provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation.
Benefits of Thermal Insulation
- Energy Efficiency: Proper insulation significantly reduces the amount of energy required to heat or cool a building, leading to lower utility bills and reduced strain on HVAC systems.
- Comfort: By maintaining consistent indoor temperatures, insulation enhances occupant comfort, eliminating cold drafts and hot spots.
- Environmental Impact: Insulating buildings reduces energy consumption, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions and the overall carbon footprint.
- Soundproofing: Many insulation materials also provide acoustic benefits, reducing noise transmission between rooms and from external sources.
Insulation Techniques and Applications
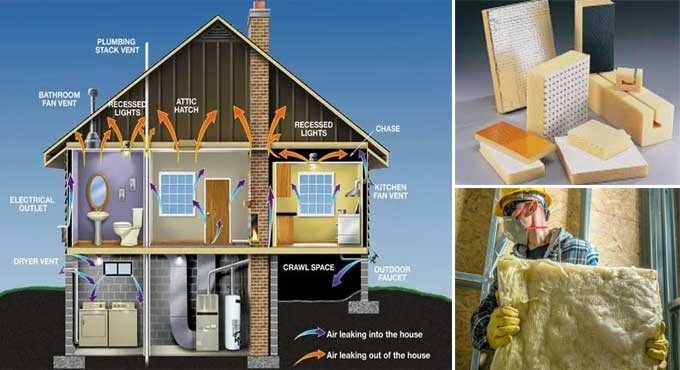
- Building Envelope: Insulating the building envelope, including walls, roofs, and floors, is crucial for minimizing heat transfer. This involves adding insulation to exterior walls, attics, and basements.
- Thermal Bridging: Addressing thermal bridges—areas where heat bypasses insulation, such as around windows, doors, and structural elements—can significantly improve overall energy efficiency.
- Air Sealing: Combining insulation with proper air sealing techniques ensures that there are no gaps or cracks through which air can escape, enhancing the effectiveness of the insulation.
- Retrofit Insulation: Existing buildings can be upgraded with additional insulation to improve energy performance. Techniques include adding insulation to attics, walls, and crawl spaces, as well as replacing or enhancing old insulation.
Innovations in Thermal Insulation
The field of thermal insulation is continually evolving, with new materials and technologies enhancing performance and sustainability:
- Aerogels: Known for their extremely low thermal conductivity, aerogels are lightweight and highly effective insulators used in specialized applications.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): These materials absorb and release thermal energy during phase transitions, providing dynamic insulation properties that adapt to temperature changes.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels (VIPs): These panels offer high insulation performance in a thin profile, making them ideal for space-constrained applications.
Conclusion
Thermal insulation is an essential aspect of modern building design and retrofitting, offering numerous benefits that enhance energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability. By selecting appropriate insulation materials, addressing thermal bridges, and incorporating advanced technologies, we can create buildings that not only meet our comfort needs but also contribute to a healthier planet. As the demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly buildings continues to grow, thermal insulation will remain a key focus for architects, builders, and homeowners alike.
Leave A Comment